What do humans definitely need for living? Water, air, nature, affection, and what else? There may be many others, and one of them is salt.
Author: t-okamoto15
Sending nice marine products
Rice is the staple food for Japanese. Not a few Japanese people would say that they could get satisfied only with white rice, even if there were no other dishes. Rice has always been indispensable in Japan’s dietary life, though there was not as much rice as in the present day to be generously served to common people.
Roads turned into farm fields!? 2
It is well known that roads in Heiankyo (ancient metropolitan Kyoto) were laid out in a grid pattern. Actually, roads were turned into farm fields, inch by inch, in many parts of Heiankyo. In the previous story, “Roads turned into farm fields!? 1”, it was described how roads were tilled and Kosho spread around the intersection of the Hachijo-dori street, which ran from east to west, and the Omiya-dori street, a little to the north of the Toji temple.
Roads turned into farm fields!? 1
Roads turned into farm fields, inch by inch, in the central metropolitan area!?
That would not occur in today’s Japan, but surprisingly happened often in the metropolitan area of medieval Kyoto (“Heiankyo”(平安京)). Was it something like rooftop greening in the present day, where people make garden park and vegetable gardens on the rooftop of buildings?
Continue reading Roads turned into farm fields!? 1Walking in Yanonosho 3 (final story in the series) – “大避神社 (Osake Jinja)” shrine as the base for worship

Present view of Osake Jinja
It is one of the traditional scenes that can be observed in most parts of Japan that residents of the same community worship Shinto or Buddhist deities as the guardians of the area, and sometimes gather in shrines or temples to enjoy festivals.
Continue reading Walking in Yanonosho 3 (final story in the series) – “大避神社 (Osake Jinja)” shrine as the base for worshipWalking in Yanonosho 2 – Looking for the local bases for ruling over Shoen (manors)

Present view of the Nakahasami Mandokoro site(中ハサミ政所)
Aioi City, Hyogo Prefecture, where Yanonosho is located, is remote from the Toji temple in Kyoto, though both are included in the Kansai region. For landowners to rule Shoen from Kyoto, they needed to establish local bases for administrative and operational affairs. Such facilities were called “Mandokoro”. For Toji, local Mandokoro were the heart of domination over Shoen. Where, then, were Toji’s Mandokoro located?
Continue reading Walking in Yanonosho 2 – Looking for the local bases for ruling over Shoen (manors)Walking in Yanonosho 1 – Where was Toji’s estate located?

Present view of the area where “Yanonosho Reimyo Nishikata” was located
Sometimes we need to visit, see, and feel a place to actually understand it. The case is the same with Shoen (manors). The Toji Hyakugo Archives include a large number of Shoen-related documents, but it is difficult to actually understand what they were like by merely reading the text written on the documents. It is also important to visit the place, walk across the area, and see the scenery of the area with one’s own eyes. The three series starting today will share with you a visit to Yanonosho(矢野荘), Harimanokuni(播磨国) (the present southwestern Hyogo Prefecture).
Continue reading Walking in Yanonosho 1 – Where was Toji’s estate located?Scary stories of stars 2
Still in the present day, we try to read horoscope, make a wish to a shooting star, and think about many things looking at stars in the night sky.
Continue reading Scary stories of stars 2Scary stories of stars 1
The term “星合 (Hoshiai)” means the Star Festival, where the two stars of Kengyu and Orihime meet with each other on the night of lunar July 7, only once every year. The Star Festival is still a popular event in the present day, colored with its romantic legend.
Identity of the boat depicted in the Taruminosho Sashizu drawing
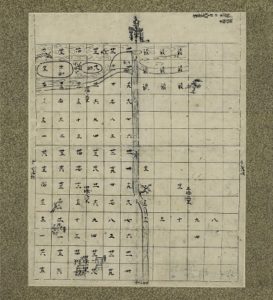
Item 101 of Box-U(Katakana), “Settsunokuni Taruminosho Sashizu”,dated October 1463
The “Settsunokuni Taruminosho Sashizu” drawing, which was featured in Nos. 26 and 27 in the Stories behind the Hyakugo Archives, was exhibited at the Kyoto Prefectural Library and Archives, in a special exhibition titled “400th Anniversary of Excavation of the Takasegawa River: Takasegawa and Water Transportation in Kyoto”. You may have a question whether it was appropriate to exhibit materials concerning the Kanzakigawa river, a branch of Yodogawa in Osaka, in an exhibition concerning water transportation in Kyoto. We hope that you will understand that these rivers are connected with each other.
Continue reading Identity of the boat depicted in the Taruminosho Sashizu drawing
Sealing the back of the paper
The back of paper is called “Shihai (shi: paper; hai: back)” Characters are sometimes written on Shihai.
This story is focused on Shihai of the document mentioned in “24. History recorded in drawings” in the Stories behind the Hyakugo Archives:

People have always loved the Matsutake mushroom in Japan!
– “They say that monks send apprentices all the way to Mt. Hira for fetching their favorite foods, such as Matsutake, Hiratake, Enoki/Nameko, Renkon that grows in ponds, Seri, Junsai, Gobo, Kohone, Udo, Warabi, Tsukushi, and so on.”
Continue reading People have always loved the Matsutake mushroom in Japan!
Shopping techniques? – Purchasing Egoma (Perilla seed) oil
A critical game or battle that may decide one’s fate is sometimes referred to as “Tennozan (天王山)”. “Tennozan” is a mountain located in Oyamazaki-cho(大山崎町) in southern Kyoto Prefecture. Hashiba Hideyoshi (羽柴秀吉) and Akechi Mitsuhide (明智光秀) fought for this mountain in their battle of Yamazaki. Hideyoshi won this mountain, and that victory determined their destinies in the entire battle. This is why a critical game or battle is called “Tennozan”.
In Oyamazaki, where Tennozan is located, the production of Egoma (荏胡麻Perilla seed) oil was prosperous. The origin of this product is believed to be traced back to the Heian period. Oil dealers were doing business around the Rikyu Hachimangu shrine (離宮八幡宮) at the foot of Tennozan, and later established a trade union called “Za”. The Oyamazaki Aburaza (lit. Oyamazaki Oil Trade Union) served Iwashimizu Hachimangu (石清水八幡宮), the main shrine for Rikyu Hachimangu, which was located across the river, and cooperated in religious services and festivals, and finally acquired exclusive rights for the procurement of raw materials, production and marketing, in return for such services.
The Egoma oil became a special product from this region, and was used for lighting lamps. It was not only delivered to Iwashimizu Hachimangu, but also marketed in Oyamazaki and in Kyoto. The Toji Hyakugo Archives records how the oil was traded:

Continue reading Shopping techniques? – Purchasing Egoma (Perilla seed) oil
Emperor’s command written on thin black paper
What are the most exciting things about ancient documents?
Deciphering cursive handwritten characters? Appreciating handwriting and brush strokes by famous persons?
The answers will vary. Studies of ancient paper used may be one of them. Today’s story is focused on paper used in ancient documents.

Continue reading Emperor’s command written on thin black paper
What are drawn in the picture? 2
Some Sashizu (drawings) are included in the Toji Hyakugo Archives. One of them is a Shoen Ezu (lit. pictorial diagram of manor) titled “Settsunokuni Taruminosho Sashizu” (Item 101 of Box-U (Katakana)).
This picture depicts a Shoen (manor) that was located in around the present Suita, Osaka, showing rivers and farm fields throughout Taruminosho. At a close look, some things are drawn between the two islands that are located in the Mikunigawa river (present Kanzakigawa river), which runs from east to west at the top of the picture.

What are drawn in the picture? 1
The Toji Hyakugo Archives include several documents titled “Sashizu (差図)”. This term sounds unfamiliar. What does it mean?
For example, the figure below is called “Settsunokuni Taruminosho Sashizu”. It seems like a kind of map. Let’s have a close look at it.
Let’s have a break now that work is done
History recorded in drawings
“Documents” contain not only text. Today, let’s look at how history is recorded in drawings.

“Iyonokuni Yugeshimanosho (伊予国弓削島荘)” was an area known for salt production, and had been widely known as a “Shoen (manor) of salt”. This manor is located on the Yugeshima island(弓削島) and the Hyakkanjima island(百貫島), Kamijima-cho(上島町), Ochi-gun(越智郡), Ehime(愛媛) in the present day, at the easternmost tip of the Geiyo Islands that range from Hiroshima Prefecture to Ehime Prefecture (Google Maps ). Turn the Sashizu (map) north up, and compare it with the present map (Geospatial Information Authority of Japan ). The L-shaped island is Yugeshima, and “辺屋路島 (Heyajijima)” drawn to the northeast of Yugeshima equals to today’s Hyakkanjima. The shapes are simplified, but clearly represent the geographic characteristics of the two islands.
Early history of Chamise (teahouses) – It was not an easy way 2
Tea vendors started to gather in the temple town in front of the Minamidaimon gate of Toji, which was crowded with many visitors.
Occasionally, those tea vendors met sudden incidents.
Continue reading Early history of Chamise (teahouses) – It was not an easy way 2
Early history of Chamise (teahouses) – It was not an easy way 1
The approaches to large temples and shrines are fringed with a number of teahouses and souvenir shops.
It was in the Muromachi period when vendors started to gather in front of temples and shrines. In those days, few merchants had shop buildings.
What, then, were teahouses in the Muromachi period like?
Continue reading Early history of Chamise (teahouses) – It was not an easy way 1